Is your DNS server not responding, leaving you unable to access the internet? This means that the decentralized naming systems responsible for turning hostnames into IP addresses failed to respond. Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll walk you through a step-by-step guide on how to fix this common issue and get back online in no time.
Having a DNS server that is not responding can be frustrating, especially when you need to access important websites or complete work tasks. There are a variety of reasons these types of DNS errors can occur. Fortunately, most of them have simple resolutions so that with a few simple troubleshooting steps, you can resolve this problem quickly and easily.
From checking your network connection to resetting your router and clearing your DNS cache, we’ll cover all the necessary steps to get your DNS server up and running again. Not only will we provide you with easy-to-follow instructions, but we’ll also explain why each step is important, so you can understand the process behind it.
So, if you’re ready to regain access to the internet and solve the DNS server not responding issue, let’s dive right in and get you back online in no time!
What is a DNS server?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a foundational technology that powers the vast majority of internet activities. Essentially, a DNS server translates website names, which are human-readable like ‘google.com’, into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network. Think of it as a digital phonebook for the internet. However, if the DNS server is unable to properly complete this name resolution process, the end result is usually a message indicating that the DNS server is not responding.
Common reasons for DNS server not responding to error
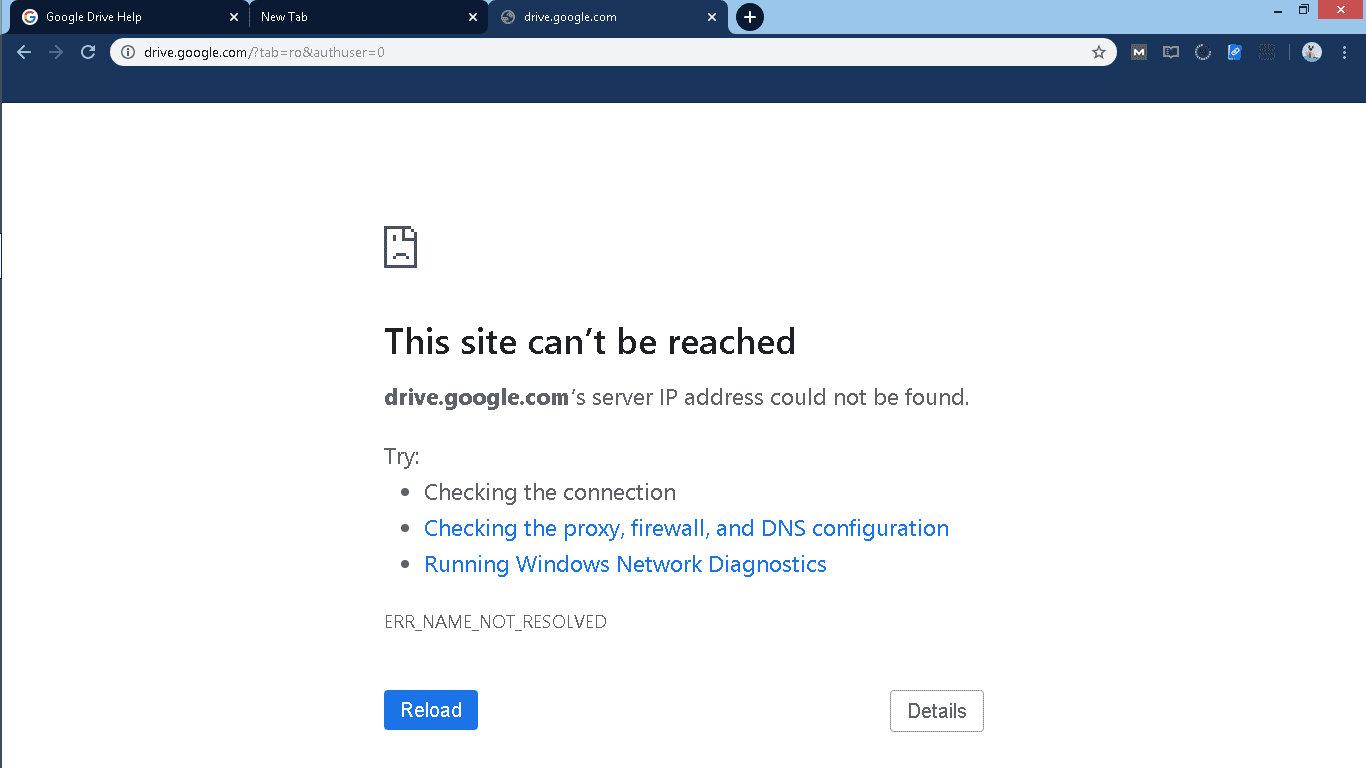
“DNS Server Not Responding” indicates that your browser couldn’t connect to the internet. Usually, DNS issues originate from the user’s side, possibly due to network or internet disruptions, incorrect DNS configurations, or an outdated browser. Sometimes, a temporary server downtime can also cause the DNS to be inaccessible. Before diving into the solutions, it’s crucial to understand the common culprits behind this error:
- Network Issues: Problems with your network connection can lead to DNS errors.
- Server Downtime: Sometimes the DNS server itself can be down.
- Firewall and Antivirus Interference: Firewalls or antivirus programs might mistakenly block DNS server requests.
- Browser Cache: Accumulated browser cache might contain corrupted files, leading to DNS errors.
- Outdated Network Drivers: Drivers facilitate communication between your OS and hardware. Outdated drivers can be problematic.
Troubleshooting steps for DNS server not responding to error
When faced with a DNS server not responding error, you don’t have to be tech-savvy to resolve it. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Switch to a different browser.
The first step would be to try accessing the webpage from an alternative browser. If your default browser is Safari or Google Chrome, try accessing the desired website via Firefox or Edge instead. If needed, ensure that your new browser is up to date. This change can often resolve browsing issues quickly and effectively.
However, if you still see the “DNS Server Not Responding” message, you can rule out your browser as the source of the issue.
Step 2: Check your internet connection
If the DNS server not responding is not caused by the browser, check if the router is the issue. To do this, verify if other devices connected to the same router can access the internet or try accessing the website using mobile data. Sometimes the issue might not be with the DNS server but with the internet connection itself.
Step 3: Restart your router and modem
Restarting your router can often fix the “DNS Server not Responding” issue. Simply press the power button on your router, unplug the power cable, wait for about 30 seconds, plug it back in, and press the power button to restart it. This issue may occur due to data traffic, and restarting the router can work wonders.
Step 4: Flush DNS cache
As with the router cache, clearing your DNS cache or resetting your IP might fix your connection issues. DNS cache memory can cause errors, so it’s important to clear it. Old entries in your DNS cache could be the cause of your problem.
On Windows, open Command Prompt and type:
ipconfig /flushdnsFor Mac users, open Terminal and type:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponderAfter this, you can restart your web browser. Doing so refreshes your browser’s cache. If you can now connect to the webpage you were having trouble with earlier, the problem is resolved. If not proceed to the next method.
Step 5: Change DNS server settings
Switching to a different DNS server like Google’s public DNS might resolve the issue.
For Windows:
- Go to the Control Panel.
- Click ‘Network and Internet‘ > ‘Network and Sharing Center‘ > ‘Change adapter settings‘.
- Right-click your active connection > ‘Properties’.
- Find and select ‘Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)‘ or ‘Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)‘ > ‘Properties‘.
- Use the IP addresses of the Google DNS servers:
- For IPv4:
8.8.8.8under Preferred DNS server and/or8.8.4.4under Alternative DNS server
- For IPv4:
For Mac:
- Go to ‘Apple menu‘ > ‘System Preferences‘ > ‘Network‘.
- Choose your active connection > ‘Advanced’ > ‘DNS’.
- Click ‘+’ and add
- For IPv4:
8.8.8.8under Preferred DNS server and/or8.8.4.4under Alternative DNS server
- For IPv4:
Step 6: Disable firewall or antivirus software temporarily
Antivirus software and firewalls are critical for safeguarding your devices, but they can sometimes cause issues that interfere with network connections. However, sometimes these programs can mistakenly block DNS requests. How can you check if a firewall or antivirus interference is the issue? You can try disabling them temporarily to see if it resolves the issue. Just remember to re-enable them immediately after testing.
Step 7: Disable IP Version 6 (IPv6)
IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol and is designed to replace IPv4, which is running out of available addresses. Disabling IPv6 can have some consequences, including potentially limiting your ability to access certain websites or services that rely on IPv6.
So I would suggest disabling IPv6 as a solution for the “DNS server is not responding” issue should generally be considered as a last resort.
Step 8: Contact your internet service provider (ISP)
If the above steps fail, your ISP might be experiencing issues. Give them a call to ascertain if they’re aware of any problems or if they can provide a solution.
A ‘DNS server not responding’ error can be a temporary hiccup or an indication of a more significant issue. With the steps outlined above, you’re well-equipped to tackle the problem and get back online. However, always consult with professionals or your ISP if you’re unsure.