Google’s Core Web Vitals have this year (2021) become a key ranking metric for the search giants.
Core Web Vitals measure various aspects of a website’s performance from page speed to responsiveness and how highly your website is ranked in search will be impacted by how well it performs against these metrics.
What are Google’s Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals are a set of three ranking factors that Google has established are the most important when it comes to providing a great user experience on your website.
Google’s Core Web Vitals fall under its Page Experience ranking signal therefore ensuring your website is performing well against the three factors will go a long way to helping you to rank well for your chosen search terms.

There are three Core Web Vitals:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This measures how long it takes for the main content on your page to load. Your main content should load within 2.5 seconds (or less).
- First Input Delay (FID): This measures how long it takes for your webpage to become interactive. Your page should be interactive within 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLD): This will score your page for any unexpected content movements. For example, if a large image loads and pushes text down the page when a user is reading it. You should aim for a score of less than 0.1.
The thing you’ll probably notice about these three metrics is that they are all user-centric. User experience is now top of Google’s list when it comes to ranking a website. If it doesn’t think a user will have a good experience using your website, for an array of reasons, then it isn’t willing to rank you within its search results…or certainly not on the first page.
The good news is that you can test your website regularly to see how it’s performing against Google’s Core Web Vitals.
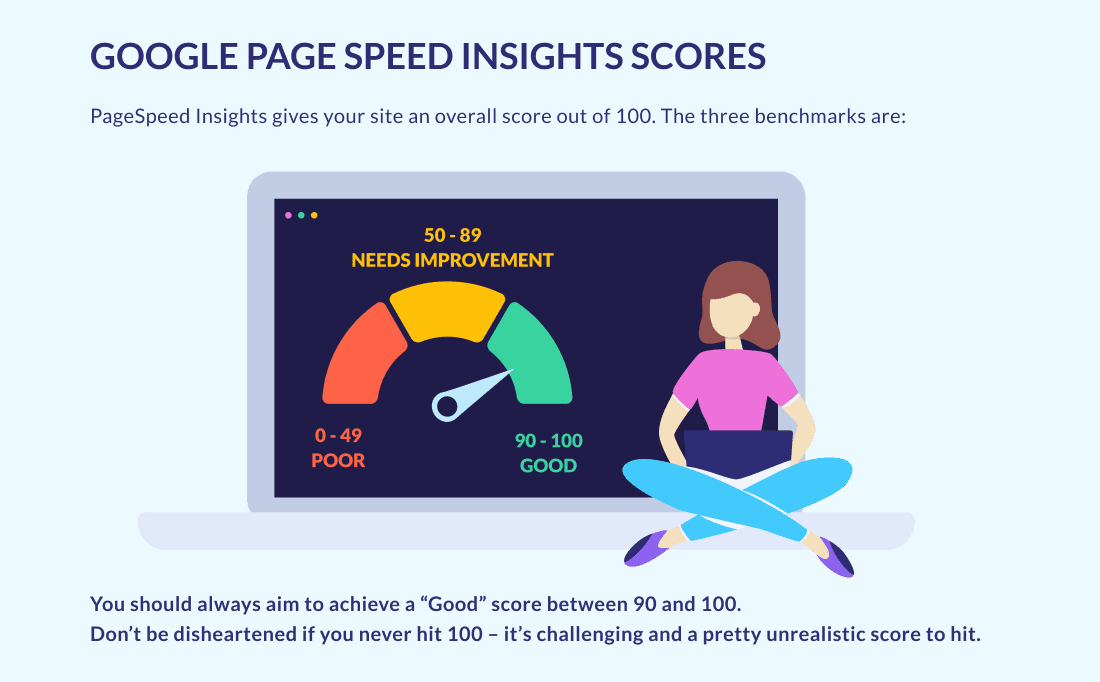
The likelihood is that you’ll have already set up a Google Search Console for your website and within the dashboard, you’ll find a Core Web Vitals Report. This will measure the performance of your website against the three factors and give you a score for each, either poor, needs improvement, or good.
So, how can you optimize your website for Google’s Core Web Vitals?
Limit Your Plugins and Apps
Plugins and apps can offer you extra functionality or design elements that you otherwise wouldn’t be able to achieve. Having too many installed and running however can be detrimental to the load speed of your website.
Take a look at the plugins you have installed and decide if you definitely need them. Often you may find that you have plugins installed that do duplicate jobs or that are out of date. It’s important to regularly audit your plugins and delete or update any that are old.
Don’t Go Overboard with Code
Put simply, the more code your website has, the longer it will take to load. Code is, of course, an essential part of building a website but you don’t need to go overboard.
For each new piece of code that you add to your website, determine if it’s essential for the function of your website first. Website builders will often load all of the possible scripts and code blocks within your website, whether you’re using them or not, which can lead to “code bloat”.
We all know how it feels to be bloated. You feel sluggish and slow. Your website is no different and if it’s too bloated with code it will function at a slower speed. Choosing simpler fonts and colors is a good first step to reducing the amount of code your website requires to run.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a place to store your website. These “storage centers” are found all over the world and users access your website via the server that is closest to them geographically.
The idea behind CDN’s is to provide users with a fast way to access your website by connecting them to the server that is closest to them.
Some website builders, such as Wix, automatically use a CDN which can help to make your website load as quickly as possible for every individual user.
Conduct Regular Mobile Tests
By now you should know the importance of a mobile-friendly website. More and more users access the internet via a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet which prompted Google to announce mobile-first indexing. This means the search engine will now use the mobile version of your website to rank you in search results.
You need to ensure your website is performing to a high standard on mobile devices and the best way to do this is by conducting regular mobile tests.
Regularly check to see how your website performs on all different devices and pay close attention to how quickly your site loads and any content shifts (CLD’s).
You can also use your PageSpeed Insights dashboard to compare how your website performs on a mobile device compared to a desktop and flag up any issues which may be slowing down the mobile version of your website.
Optimize Your Images
Your images are often one of the largest pieces of content that your website needs to load therefore optimizing them can help to reduce their file size, in turn speeding up your website.
Some top tips for optimizing images include:
- Ensure you select the right file type.
- Compress your images before uploading them to your website builder.
- Only include images that will add value to the user and improve the user experience of your website.
The bigger your image files, the longer they’ll take to load, therefore keeping your image sizes low is a key step to improving the load speed of your website.
In Summary
If you want to rank well in Google’s search results for your target search terms then you need to incorporate the Core Web Vitals into your SEO strategy.
Google’s Core Web Vitals feed into the search engines Page Experience ranking signal alongside other factors such as website security and mobile responsiveness.
Google has been clear that these three factors will play a major part in ranking websites moving forward therefore you simply can’t afford to ignore them.