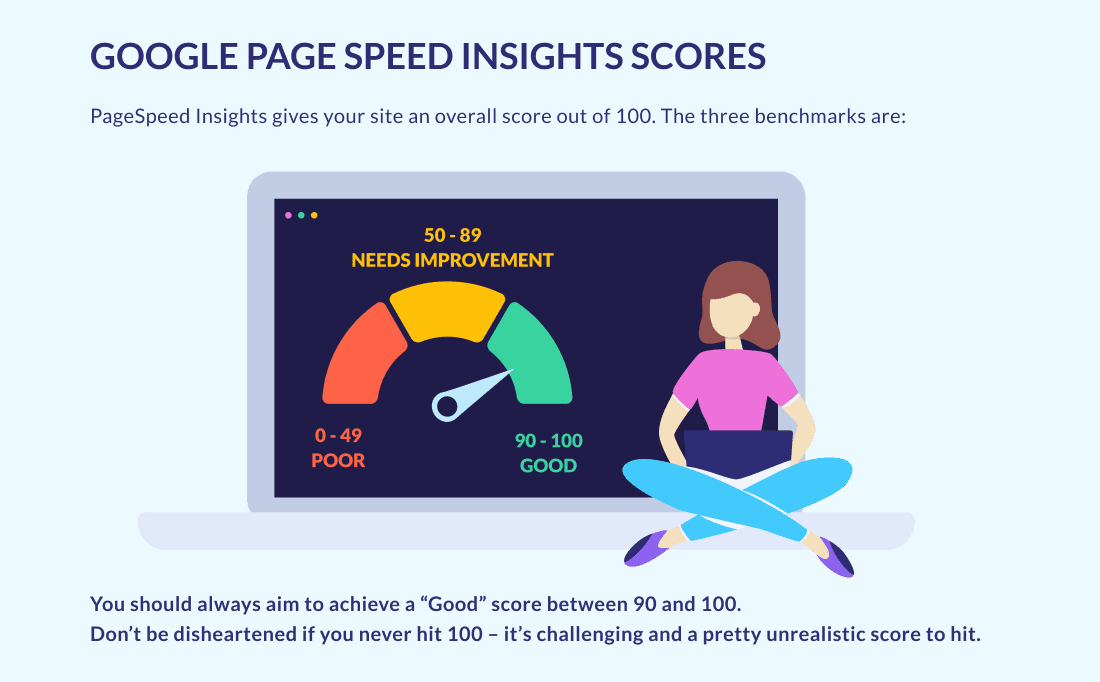
Google is the primary gateway for users seeking information, services, and products in the vast internet landscape. Adhering to its guidelines is paramount for websites aspiring to rank high in Google search results. However, in the pursuit of visibility, some websites resort to manipulative tactics that violate Google’s quality standards.
When Google detects such violations, it takes action to ensure a fair and reliable search experience. One of the severe penalties websites may face is the “Pure Spam” manual action. In this blog post, we’ll delve into what Google Pure Spam Manual Action entails, its potential causes, and actionable strategies for recovery.
Understanding Google Pure Spam Manual Action
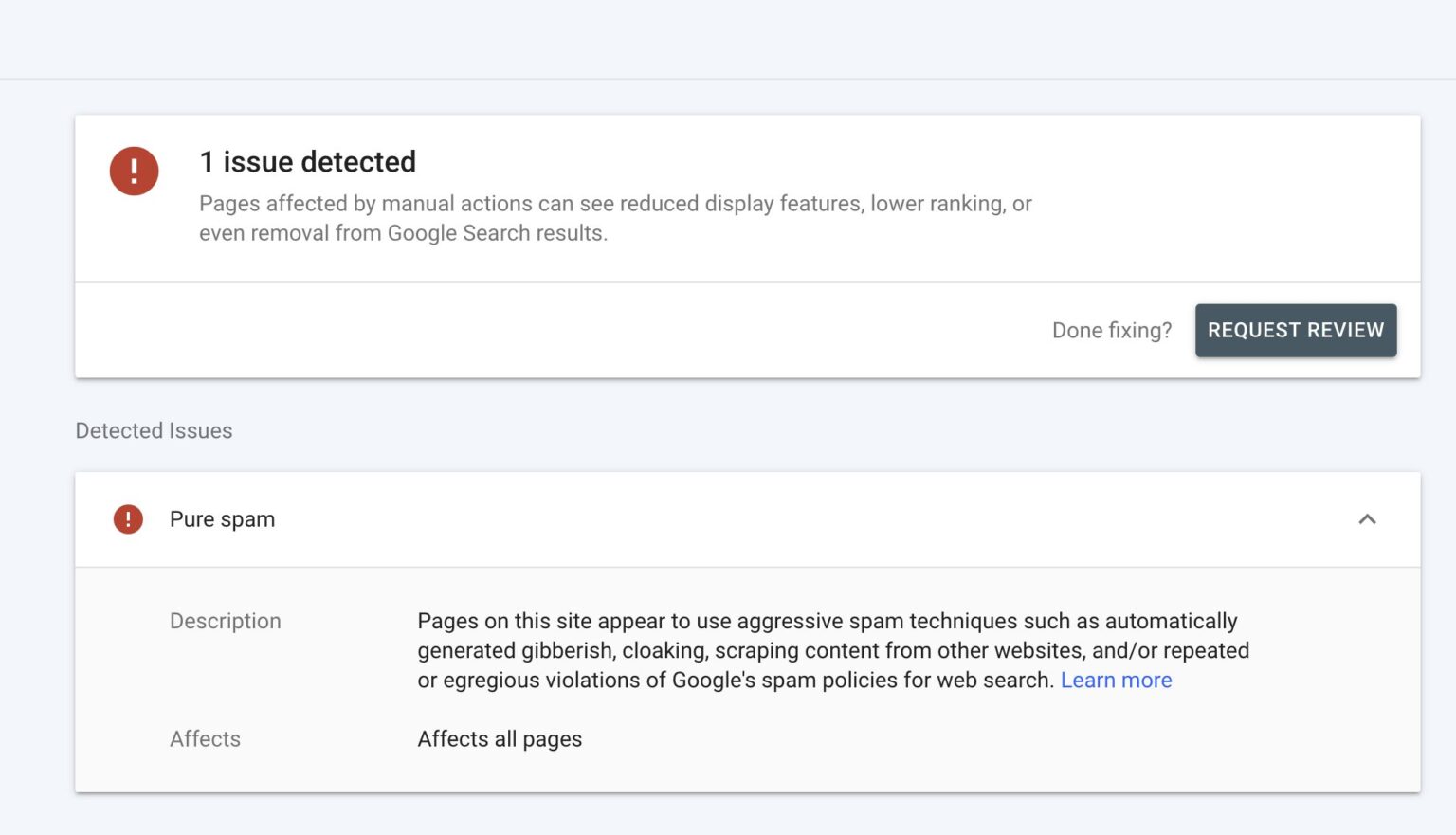
Google’s Pure Spam Manual Action is a severe penalty imposed on websites that violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. When Google’s human reviewers manually identify a website as indulging in pure spam, they take decisive action to protect the integrity of search results. This action entails removing the offending website from Google’s index, rendering it virtually invisible to users searching via Google.
Pure spam encompasses a variety of deceptive practices aimed at manipulating search rankings, such as:
- Keyword stuffing: Deliberate overuse of keywords to manipulate search engine rankings, often resulting in unnatural and unreadable content.
- Cloaking: Presenting different content to search engines and users, deceiving search engine crawlers to achieve higher rankings.
- Hidden text or links: Concealing text or links within a webpage to manipulate rankings, often by making them the same color as the background or positioning them off-screen.
- Sneaky redirects: Redirecting users to a different page than the one they initially requested, typically to a page unrelated to the search query.
- Automated or scraped content: Publishing content generated automatically or from other sources without adding substantial value.
- Malicious behavior: Engaging in phishing, distributing malware, or participating in link schemes to manipulate search rankings.
Causes of Pure Spam Manual Action
Websites can incur Pure Spam Manual Action for various reasons, often stemming from a blatant disregard for Google’s quality guidelines. Some common causes include:
- Black Hat SEO Tactics: Using black hat SEO techniques to artificially inflate rankings, such as buying links or employing link farms.
- Content Quality Issues: Publishing low-quality, thin, or duplicate content that adds little or no value to users.
- Unnatural Link Building: Acquiring many low-quality or irrelevant backlinks through manipulative tactics, such as link exchanges or paid links.
- Malware or Security Breaches: Hosting malware or engaging in malicious behavior that compromises user security.
- Algorithmic Penalties: Being affected by algorithm updates like Google’s Panda or Penguin, which target low-quality content and spammy link practices.
Steps to Recover from Pure Spam Manual Action
Recovering from a Pure Spam Manual Action requires a comprehensive strategy to rectify the underlying issues and demonstrate a commitment to compliance with Google’s guidelines. While recovery can be challenging, following these steps can increase your chances of reinstatement:
Identify the Violations
Begin by thoroughly analyzing your website to identify any violations of Google’s guidelines. This may involve conducting a content audit, evaluating backlink profiles, and reviewing technical aspects of your website for issues like cloaking or hidden text.
Address Content Quality
Remove or improve any low-quality, duplicate, or irrelevant content on your website. Focus on creating high-quality, unique content that provides value to users and aligns with their search intent.
Resolve Technical Issues
Fix any technical issues on your website that may have contributed to the Pure Spam Manual Action. This includes eliminating hidden text, removing sneaky redirects, and ensuring compliance with Google’s webmaster guidelines.
Audit Backlink Profile
Evaluate your website’s backlink profile to identify and disavow any spammy or unnatural links. Use Google Search Console and third-party tools to identify potentially harmful backlinks and take necessary action to disavow them.
Submit a Reconsideration Request
Once you’ve addressed the violations and made substantial improvements to your website, submit a reconsideration request through Google Search Console. Clearly outline the steps you’ve taken to rectify the issues and demonstrate your commitment to compliance with Google’s guidelines.
Documentation
If applicable, provide documentation or evidence supporting your reconsideration request. This may include details of content improvements, actions taken to remove spammy backlinks, and proof of security measures implemented to safeguard against malware.
Be Patient and Persistent
Recovery from a Pure Spam Manual Action can be time-consuming, and Google’s review of reconsideration requests may take several weeks. Be patient and continue to monitor your website’s performance while awaiting a response from Google.
Maintain Compliance
Once your website has been reinstated, prioritize compliance with Google’s guidelines to prevent future penalties. Monitor your website regularly for potential violations and stay informed about updates to Google’s algorithms and procedures.
Conclusion
Google’s Pure Spam Manual Action is a powerful deterrent against websites, including an SEO company, that use manipulative tactics to deceive users and manipulate search rankings. While recovering from a Pure Spam Manual Action can be challenging, it’s not insurmountable. By diligently addressing the underlying issues, making necessary improvements to your website, and demonstrating a commitment to compliance with Google’s guidelines, you can increase your chances of reinstatement and regain visibility in Google search results. Maintaining a website that prioritizes user experience, content quality, and ethical SEO practices is vital to long-term success in the digital landscape.